Abstract
Review Article
Rhabdomyoblasts in Pediatric Tumors: A Review with Emphasis on their Diagnostic Utility
Giuseppe Angelico*, Eliana Piombino, Giuseppe Broggi, Fabio Motta and Saveria Spadola
Published: 09 March, 2017 | Volume 1 - Issue 1 | Pages: 008-016
Rhabdomyosarcoma is a soft tissue pediatric sarcoma composed of cells which show morphological, immunohistochemical and ultrastructural evidence of skeletal muscle differentiation. To date four major subtypes have been recognized: embryonal, alveolar, spindle cell/sclerosing and pleomorphic. All these subtypes are defined, at least in part, by the presence of rhabdomyoblasts, i.e. cells with variable shape, densely eosinophilic cytoplasm with occasional cytoplasmic cross-striations and eccentric round nuclei. It must be remembered, however, that several benign and malignant pediatric tumours other than rhabdomyosarcoma may exhibit rhabdomyoblaststic and skeletal muscle differentiation. This review focuses on the most common malignant pediatric neoplasm that may exhibit rhabdomyoblastic differentiation, with an emphasis on the most important clinicopathological and differential diagnostic considerations.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.jsctt.1001002 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Rhabdomyosarcoma; Nephroblastoma; Malignant triton tumor; Pleuropulmonary blastoma; Rhabdomyoblast
References
- Parham DM, Barr FG. Classification of rhabdomyosarcoma and its molecular basis. Adv Anat Pathol. 2013; 20: 387-397. Ref.: https://goo.gl/sUAFuX
- Parham DM, Ellison DA. Rhabdomyosarcomas in adults and children: an update. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2006; 130: 1454-1465. Ref.: https://goo.gl/S8vwk7
- Miettinen M, Fetsch JF, Antonescu CR. Tumors with skeletal muscle differentiation. AFIP atlas of tumor pathology: tumors of the soft tissues. Silver Spring: ARP Press. 2014; 289-308.
- Woodruff JM, Perino G. Non-germ-cell or teratomatous malignant tumors showing additional rhabdomyoblastic differentiation, with emphasis on the malignant Triton tumor. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1994; 11: 69-81. Ref.: https://goo.gl/rg8lUB
- Fletcher CDM. Spindle cell/sclerosing rhabdomyosarcoma. World Health Organization (WHO) classification of tumours of soft tissue and bone. Vol 5. Fourth Edn. IARC press: France, Lyon, 2013; 468.
- Qualman SJ, Coffin CM, Newton WA, Hojo H, Triche TJ, et al. Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study: update for pathologists. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 1998; 1: 550-61. Ref.: https://goo.gl/PS6z00
- Cavazzana AO, Schmidt D, Ninfo V, Harms D, Tollot M, et al. Spindle cellrhabdomyosarcoma. A prognostically favorable variant of rhabdomyosarcoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1992; 16: 229-235. Ref.: https://goo.gl/UzGfAW
- Folpe AL, McKenney JK, Bridge JA, Weiss SW. Sclerosing rhabdomyosarcoma in adults: report of four cases of a hyalinizing, matrix-rich variant of rhabdomyosarcoma that may be confused with osteosarcoma, chondrosarcoma, or angiosarcoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2002; 26: 1175-1183. Ref.: https://goo.gl/4ipwjA
- Rekhi B, Upadhyay P, Ramteke MP, Dutt A. MYOD1 (L122R) mutations are associated with spindle cell and sclerosing rhabdomyosarcomas with aggressive clinical outcomes. Mod Pathol. 2016; 29: 1532-1540. Ref.: https://goo.gl/be0R7M
- Mungan S, Arslan S, Küçüktülü E, Ersöz Ş, Çobanoğlu B. Pleomorphic Rhabdomyosarcoma Arising from True Vocal Fold of Larynx: Report of a Rare Case and Literature Review. Case Rep Otolaryngol. 2016; 2016: 8135967. Ref.: https://goo.gl/6E9E7H
- Rudzinski ER, Anderson JR, Lyden ER, Bridge JA, Barr FG, et al. Myogenin, AP2β, NOS-1, and HMGA2 are surrogate markers of fusion status in rhabdomyosarcoma: a report from the soft tissue sarcoma committee of the children's oncology group. Am J Surg Pathol. 2014; 38: 654-659. Ref.: https://goo.gl/44GfNS
- Miki H, Kobayashi S, Kushida Y, Sasaki M, Haba R, et al. A case of infantile rhabdomyofibrosarcoma with immunohistochemical, electronmicroscopical, and genetic analyses. Hum Pathol. 1999; 30: 1519-1522. Ref.: https://goo.gl/XrNi6K
- Lundgren L, Angervall L, Stenman G, Kindblom LG. Infantile rhabdomyofibrosarcoma: a high-grade sarcoma distinguishable from infantile fibrosarcoma and rhabdomyosarcoma. Hum Pathol. 1993; 24: 785-795. Ref.: https://goo.gl/KmOrQD
- Stasik CJ, Tawfik O. Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor with rhabdomyosarcomatous differentiation (malignant triton tumor). Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2006, 130: 1878-1881. Ref.: https://goo.gl/8BLODr
- Durbin AD, Ki DH, He S, Look AT. Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016; 916: 495-530. Ref.: https://goo.gl/n8eirv
- Masson P. Recklinghausen’s neurofibromatosis, sensory neuromas and motor neuromas. In: Libman Anniversary. Vol 2. New York, NY: International Press. 1932: 793-802.
- Woodruff JM, Perino G. Non-germ-cell or teratomatous malignant tumors showing additional rhabdomyoblastic differentiation, with emphasis on the malignant triton tumor. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1994; 11: 69-81. Ref.: https://goo.gl/rTiRHj
- Karcioglu Z, Someren A, Mathes SJ. Ectomesenchymoma. A malignant tumor of migratory neural crest (ectomesenchyme) remnants showing ganglionic, schwannian, melanocytic and rhabdomyoblastic differentiation. Cancer. 1977; 39: 2486-2496. Ref.: https://goo.gl/dR4vdr
- Huang SC, Alaggio R, Sung YS, Chen CL, Zhang L, et al. Frequent HRAS Mutations in Malignant Ectomesenchymoma: Overlapping Genetic Abnormalities with Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2016; 40: 876-885. Ref.: https://goo.gl/cbhfNV
- Chau YY, Hastie ND. The role of Wt1 in regulating mesenchyme in cancer, development, and tissue homeostasis. Trends Genet. 2012; 28: 515-524. Ref.: https://goo.gl/gBcxA1
- Salvatorelli L, Parenti R, Leone G, Musumeci G, Vasquez E, et al. Wilms tumor 1 (WT1) protein: Diagnostic utility in pediatric tumors. Acta Histochem. 2015; 117: 367-378. Ref.: https://goo.gl/Cy7A8U
- Tu BW, Ye WJ, Li YH. Botryoid Wilms' tumor: report of two cases. World J Pediatr. 2011; 7: 274-276. Ref.: https://goo.gl/enFS3P
- Carpentieri DF, Nichols K, Chou PM, Matthews M, Pawel B, et al. The expression of WT1 in the differentiation of rhabdomyosarcoma from other pediatric small round blue cell tumors. Mod Pathol. 2002; 15: 1080-1086. Ref.: https://goo.gl/JH5dM6
- Pollono D, Drut R, Tomarchio S, Fontana A, Ibañez O. Fetal rhabdomyomatous nephroblastoma: report of 14 cases confirming chemotherapy resistance. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2003; 25: 640-643. Ref.: https://goo.gl/NKaglc
- Irtan S, Ehrlich PF, Pritchard-Jones K. Wilms tumor: "State-of-the-art" update, 2016. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2016; 25: 250-256. Ref.: https://goo.gl/nKgxCA
- Cone EB, Dalton SS, Van Noord M, Tracy ET, Rice HE, et al. Biomarkers for Wilms Tumor: A Systematic Review. J Urol. 2016; 196: 1530-1535. Ref.: https://goo.gl/8XxcXX
- Fosdal MB. Pleuropulmonary blastoma. J Pediatr Oncol Nurs. 2008; 25: 295-302. Ref.: https://goo.gl/AFy4I5
- Mehraein Y, Schmid I, Eggert M, Kohlhase J, Steinlein OK. DICER1 syndrome can mimic different genetic tumor predispositions. Cancer Lett. 2016; 370: 275-278. Ref.: https://goo.gl/rFlSyv
- Hill DA, Jarzembowski JA, Priest JR, Williams G, Schoettler P, et al. Type I pleuropulmonary blastoma: pathology and biology study of 51 cases from the international pleuropulmonary blastoma registry. Am J Surg Pathol. 2008; 32: 282-295. Ref.: https://goo.gl/W3ANsO
- Sciot R, Dal Cin P, Brock P, Moerman P, Van Damme B, et al. Pleuropulmonary blastoma (pulmonary blastoma of childhood): genetic link with other embryonal malignancies? Histopathology. 1994; 24: 559-563. Ref.: https://goo.gl/XjHWbI
- Indolfi P, Bisogno G, Casale F, Cecchetto G, De Salvo G, et al. Prognostic factors in pleuro-pulmonary blastoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2007; 48: 318-23. Ref.: https://goo.gl/1HwiOh
Figures:
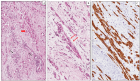
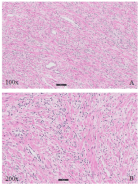
Figure 1
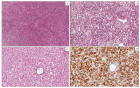
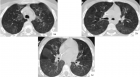
Figure 2
Similar Articles
-
Rhabdomyoblasts in Pediatric Tumors: A Review with Emphasis on their Diagnostic UtilityGiuseppe Angelico*,Eliana Piombino,Giuseppe Broggi,Fabio Motta,Saveria Spadola. Rhabdomyoblasts in Pediatric Tumors: A Review with Emphasis on their Diagnostic Utility . . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsctt.1001002; 1: 008-016
Recently Viewed
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Improvement of the Cognitive Abilities in a Chronic Generalized Anxiety Disorder and Moderate Depression Case using a Novel Integrated Approach: The Cognitome ProgramMohita Shrivastava*. Improvement of the Cognitive Abilities in a Chronic Generalized Anxiety Disorder and Moderate Depression Case using a Novel Integrated Approach: The Cognitome Program. J Neurosci Neurol Disord. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jnnd.1001100; 8: 069-089
-
Neuroprotective Effect of 7,8-dihydroxyflavone in a Mouse Model of HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorder (HAND)Tapas K Makar, Joseph Bryant, Bosung Shim, Kaspar Keledjian, Harry Davis, Manik Ghosh, Ajay Koirala, Ishani Ghosh, Shreya Makar, Alonso Heredia, Malcolm Lane, J Marc Simard, Robert C Gallo, Volodymyr Gerzanich*, Istvan Merchenthaler*. Neuroprotective Effect of 7,8-dihydroxyflavone in a Mouse Model of HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorder (HAND). J Neurosci Neurol Disord. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jnnd.1001101; 8: 090-105
-
Adult Neurogenesis: A Review of Current Perspectives and Implications for Neuroscience ResearchAlex, Gideon S*,Olanrewaju Oluwaseun Oke,Joy Wilberforce Ekokojde,Tolulope Judah Gbayisomore,Martina C. Anene-Ogbe,Farounbi Glory,Joshua Ayodele Yusuf. Adult Neurogenesis: A Review of Current Perspectives and Implications for Neuroscience Research. J Neurosci Neurol Disord. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jnnd.1001102; 8: 106-114
-
Analysis of Psychological and Physiological Responses to Snoezelen Multisensory StimulationLucia Ludvigh Cintulova,Jerzy Rottermund,Zuzana Budayova. Analysis of Psychological and Physiological Responses to Snoezelen Multisensory Stimulation. J Neurosci Neurol Disord. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jnnd.1001103; 8: 115-125
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."